Across many lands, diverse communities have long organized their cherished services of protection and justice according to particular needs, histories, and values. Regardless of structure, all such noble works require strong yet supple bonds of cooperation and trust with those served.
In an era where some face barriers separating them from critical aid, a renewed focus on coherent coordination ensures all people feel secure accessing advocates attentive to diverse voices. Just as taxpayers sustain this work through shared sacrifice, so officers commit to prudent stewardship and advancing the welfare of all.
Now more than ever, champions recognize each person deserves full knowledge of – and recourse regarding – systems established for the well-being of all. As relationships strengthen between neighborhoods and guardians through compassionate partnership, so too will the resilience of democratic traditions upholding the dignity of every life.
Principles of Democratic Policing
- Community focus: Democratic police exist to help neighborhoods stay safe and peaceful. They work directly with people through open talks to address what matters most to each area.
- Follow the rules: For the public to have confidence, cops must stick to what the law says as well as use common sense and fairness when applying rules and guidelines to different situations.
- Respect for all: Protecting basic rights is key so everyone can feel comfortable living here freely. Departments make sure their training and work equally serve folks from everywhere to keep this place united.
- Earn trust with integrity: Over time, people will believe in an honest department that does the right thing, makes its thought process transparent, and accepts responsibility when mistakes happen. Recognizing room for improvement and adapting based on community also builds faith.
Challenges and Opportunities

- A Clean house: A department can’t have the public’s or their own people’s trust if some are crooked. That kind of stuff brings down morale, wastes time and money, and stops cops from doing their jobs well. Gotta deal with it head-on.
- Team up with neighbors: Smarter policing means really connecting with the community, having open chats about concerns, and working as a team to stop crime before it starts. People will support you more when they feel heard and involved.
- Tech tools and privacy: New gadgets can give officers helpful evidence and ways to do their jobs more efficiently. But this stuff also comes with worries about people’s privacy and personal info. Departments need to use tech to help, not harm, or nobody will feel safe anymore. There’s work to do to find the right balance.
The Role of Governments and Institutional Change

- Police for democracy: It’s important the government sees police as the guardians of people’s democratic freedoms and well-being. Clear rules and groups need to exist so everyone can be sure officers are acting with integrity according to the law.
- Change from the inside: Constructive change is about more than just following new guidelines – the whole organization has to update what it stands for. That means rethinking how command works, how new recruits are trained, and how officers are reviewed to make sure the community is the top priority. An open, empathetic culture where everyone cooperates is what really protects people.
Balancing Autonomy and Oversight
Law enforcement requires discretion to respond nimbly, yet unfettered power could enable issues over time if left unexamined. Striking the right oversight balance is paramount.
Independent review provides transparency into real operations and community impacts, addressing legitimate complaints respectfully. This enhances integrity and service commitment.
Through open discussion, various viewpoints on calibrating approaches can be understood. The aim, it seems, should be uniting people in pursuit of safeguarding rights and security for all citizens. Intentional efforts toward transparency and responsiveness to the public are important to consider.
No system will be perfect, but continuous self-reflection helps identify areas for refinement. If all engaged in these complex issues in good faith, intelligently crafting collaborative solutions, that would maximize protection and justice. The well-being of communities should be the guiding focus.
Engaging with Youth and Future Generations
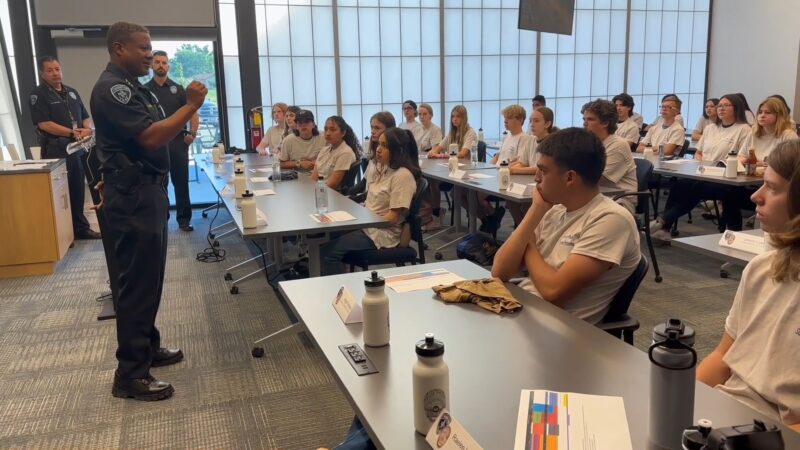

Young people will steer the course of every society tomorrow. How they view law enforcement today inevitably molds the relationship between protectors and protected years ahead.
Constructive engagement with youth, comprehending their perspective, and elucidating an officer’s duties are therefore paramount to cultivating respect and trust over the long term.
Educational settings can seed discussions where uniform and student exchange views openly, dispelling assumptions to reinforce common ground. Moreover, involving adolescents in community-focused initiatives taps their fresh outlook, zeal and creativity.
Such participation bridges comprehension across age divides now while fostering transfer of democratic policing principles into generations yet to come. With care and effort from all, the future strength of safe, just communities may continue growing from each new mind and heart guided by these shared noble purposes.
Final Words
In the end, strong relations between communities and their protectors are critical to a fair system. For policing to best serve the people, key things must be in place. Prioritizing safety, holding all sides accountable, respecting individual rights, and keeping an open flow of information help build trust that’s so important.
As times change and new challenges emerge, law enforcement needs to change along with it. That means using new technology smartly, actively engaging with residents, and leading with integrity. When many perspectives are part of the solution, it results in better outcomes for all in the long run.
Governing bodies have a clear role in setting up institutions that not only keep order, but also align with democratic values like impartiality, fairness and respect for human dignity.